Navigating Troubled Waters “The Alarming Impact of Soaring Ocean Temperatures on Shipping”

24th August 2023
Introduction: Rising Ocean Temperatures
In recent years, the world has been grappling with the devastating consequences of climate change, and one of its most ominous indicators is the rapid rising ocean temperatures. While the impacts of warming oceans are widely acknowledged, an industry that is particularly vulnerable to this phenomenon is shipping. With oceans acting as the lifeline of global trade, the warming waters pose a multifaceted threat to the shipping industry, affecting everything from operational efficiency to environmental sustainability. This article delves into the specific reasons why shipping should be deeply concerned about the soaring ocean temperatures and the steps that need to be taken to navigate these troubled waters. These changes in weather patterns threaten the entire shipping industry – vessel owners and operators, cargo owners, and ports. There are also knock-on effects on global supply chains that could affect economies more broadly. Global warming is creating more freak waves, more ferocious and sudden storms far out to sea. Ship designs and cargo configuration of the future will need to absorb these fast-changing weather patterns.

Factors affecting the Shipping industries
1. Impact on Fuel Efficiency and Costs
Shipping is a complex ecosystem that relies heavily on fuel consumption. As ocean temperatures rise, several factors come into play that undermine the fuel efficiency of vessels. Warmer waters reduce the density of seawater, affecting the buoyancy of ships and thus increasing their fuel consumption. Moreover, elevated temperatures can lead to decreased engine efficiency, prompting ships to burn more fuel to maintain their desired speeds. This double whammy not only drives up operational costs for shipping companies but also contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating the climate crisis.
2.Hull Fouling and Maintenance Challenges
Soaring ocean temperatures create an ideal environment for the proliferation of marine organisms such as barnacles, algae, and mussels on the hulls of ships. This phenomenon, known as biofouling, increases drag and reduces the hydrodynamic efficiency of vessels. As a result, ships have to exert more energy to overcome this resistance, once again leading to higher fuel consumption and maintenance costs. To counteract these effects, ships are often required to undergo more frequent and thorough cleaning, involving the use of anti-fouling coatings and underwater cleaning mechanisms. However, these practices can introduce toxic substances into the marine ecosystem, causing additional environmental concerns.
3.Disrupted Trade Routes and Increased Storm Risks
The warming of oceans contributes to the intensification of weather patterns and the increased frequency of extreme weather events, including hurricanes and typhoons. Such conditions pose a significant threat to maritime safety, potentially leading to shipwrecks, cargo losses, and even loss of human lives. Additionally, the changing climate could alter traditional trade routes as melting polar ice opens up new passages in the Arctic region. While this might offer shorter routes for some shipments, it introduces new challenges due to unpredictable ice conditions, lack of infrastructure, and potential environmental damage to this delicate ecosystem. The shipping industry and climate at Seas is at Risk, alluded to recent research from Oxford University’s Environmental Change Institute which estimates that more than $122bn of economic activity including $81bn in international trade is at risk from the impact of extreme climate events per year.
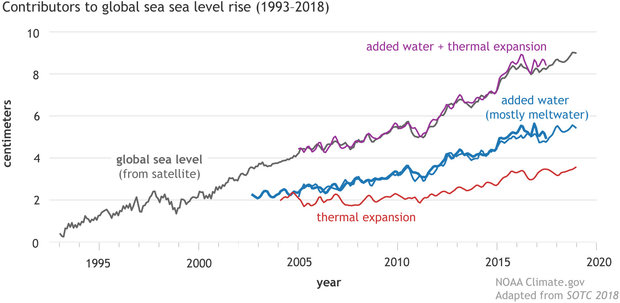
4.Rising Sea Levels and Port Infrastructure Vulnerability
One of the most concerning aspects of global warming is the rise in sea levels, primarily driven by the melting of glaciers and the expansion of seawater as it warms. This poses a direct threat to port infrastructure located in low-lying coastal areas. Many major ports around the world are susceptible to flooding and damage due to sea-level rise and the increased frequency of storm surges. The destruction of port facilities not only disrupts shipping operations but also has broader economic implications, affecting the movement of goods and global supply chains. Furthermore, the rising sea levels due to high temperatures might require substantial work on raising the heights of port terminals. Ocean Conservancy noted that raising the height of existing port terminals alone could cost more than $63bn by the end of the century.
5. Regulatory Pressures and Sustainability Demands
As the world shifts its focus toward sustainability, the shipping industry faces increasing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint. International bodies such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) are implementing stricter regulations to curb emissions from ships, including those related to greenhouse gases and air pollutants. The global sulphur cap regulation imposed in 2020 by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) have cut ships’ sulphur pollution by more than 80% and improved air quality worldwide. The reduction has also lessened the effect of sulphate particles in seeding and brightening the distinctive low-lying, disappearing reflective clouds that follow in the wake of ships so called ship tracks and help cool the planet. The warming oceans only amplify the urgency of adhering to these regulations. Shipping companies are being pushed to adopt cleaner technologies, such as alternative fuels and improved engine designs, to mitigate their contribution to climate change. Failure to do so could result in financial penalties, reputational damage, and restricted access to certain ports.
Conclusion
The shipping industry stands at a critical juncture where the escalating ocean temperatures demand swift and decisive action. The challenges posed by rising sea temperatures are multifaceted, impacting fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, trade routes, maritime safety, port infrastructure, and regulatory compliance. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from governments, industry stakeholders, and international organizations.
Shipping companies must invest in innovative technologies that enhance fuel efficiency, minimize biofouling, and adapt to changing trade routes. They should also prioritize sustainable practices to reduce emissions and minimize their ecological impact. Governments need to provide incentives for greener shipping practices and invest in the resilience of coastal infrastructure. Furthermore, international cooperation is vital to implement and enforce regulations that ensure the sustainable growth of the industry.
In the face of soaring ocean temperatures, the shipping industry can no longer remain passive. It must embrace the urgent need for adaptation and transformation, not only for its own survival but also for the health of our oceans and the planet as a whole. Only through collaborative efforts can we hope to navigate these troubled waters and secure a sustainable future for global shipping.
Click here to join our Telegram chanel
You will get information, news, and support related to Merchant Navy.
