Panama Canal Operations Navigate Challenges Across Shipping Segments

2nd August 2023
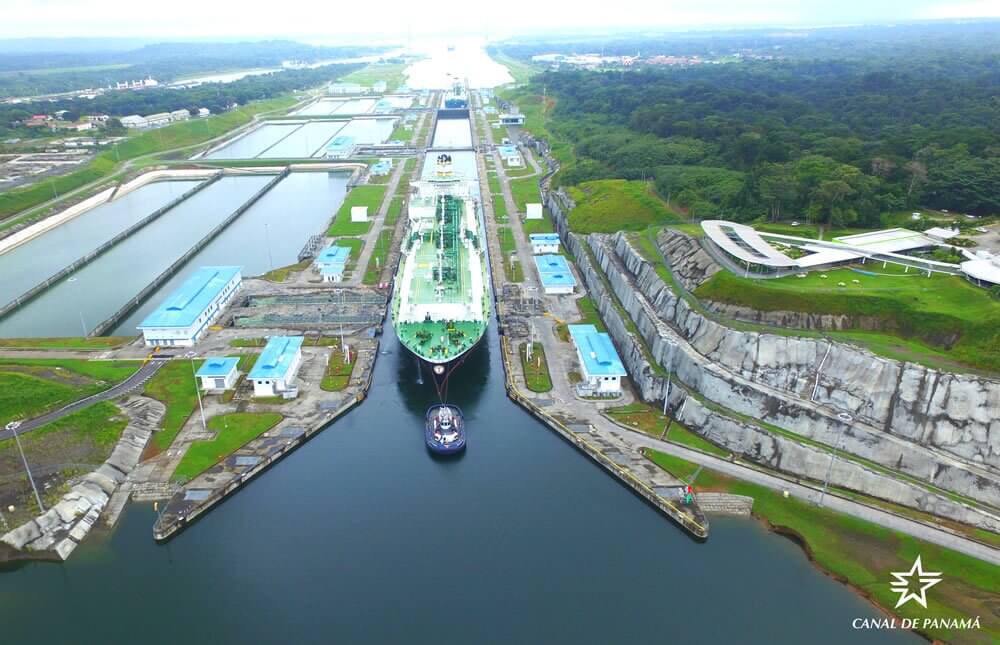
The Panama Canal, one of the world’s most vital maritime arteries, is currently facing unprecedented challenges that are rippling through every shipping segment. From container ships to bulk carriers and liquefied natural gas (LNG) tankers, each sector is feeling the impact of a rapidly evolving global landscape. In this article, we delve into the latest developments and how they are affecting each shipping segment.
Container Shipping
Container shipping, a cornerstone of global trade, has been significantly affected by the ongoing disruptions in the Panama Canal. The rise in container traffic, primarily driven by e-commerce, has exacerbated congestion issues and strained the Canal’s capacity. Vessels are facing longer waiting times, leading to delays in delivering goods worldwide. This is particularly problematic for time-sensitive shipments and industries reliant on just-in-time inventory systems.
Furthermore, container ships are grappling with a shortage of empty containers in some cases, leading to supply chain bottlenecks. Shippers are also navigating soaring transportation costs due to the increased demand for container space. These challenges are forcing companies to reevaluate their supply chain strategies, consider alternative routes, and even invest in larger vessels capable of traversing the expanded Canal.

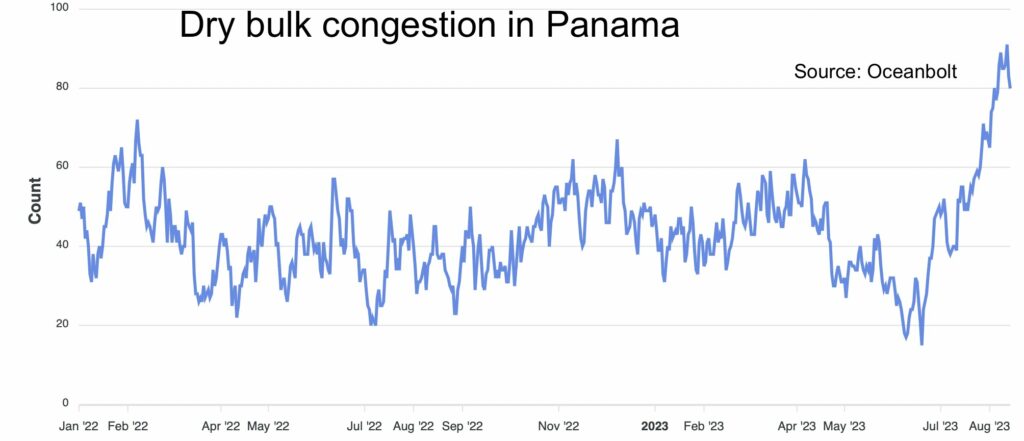
Bulk Carriers
Bulk carriers, responsible for transporting commodities such as grains, ore, and coal, have faced their own set of challenges. The Panama Canal’s draft restrictions, which limit the maximum depth of vessels that can pass through, have made it difficult for larger bulk carriers to utilize the Canal fully. This has led to increased shipping costs, as many vessels opt for longer routes around South America, like the Cape of Good Hope.
Additionally, the Canal’s restrictions have prompted some countries to explore alternative trade routes. For example, Brazil has been investing heavily in expanding its northern ports, which could provide a competitive alternative to the Panama Canal for exporting grains and other bulk commodities. While these investments will take time to materialize fully, they could reshape the global bulk shipping industry in the long term.
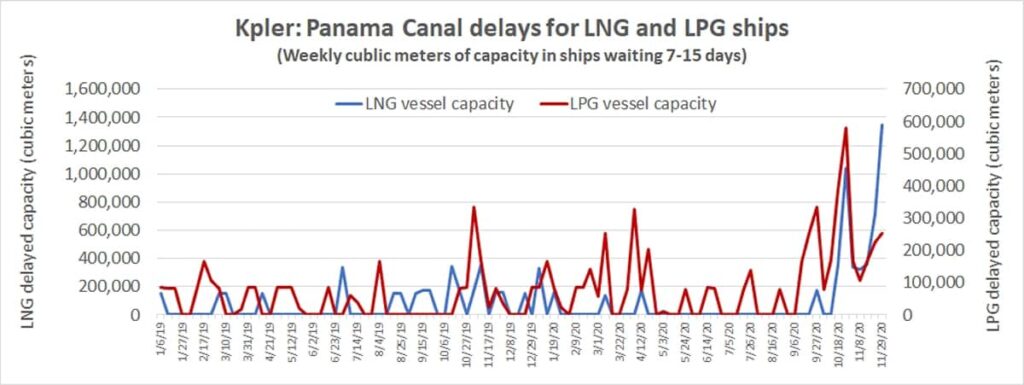
LNG Tankers
The LNG industry, which has seen significant growth in recent years, relies on the Panama Canal for expedited shipments from the United States Gulf Coast to markets in Asia and the Pacific. However, LNG tankers have faced challenges related to the Canal’s limitations, particularly with regards to vessel size.
Larger LNG carriers require deeper draft allowances, which the Canal struggles to accommodate. As a result, many LNG shipments have had to bypass the Canal, opting for longer routes around South America. This not only increases transit times but also adds to fuel costs and environmental concerns.
To address this issue, Panama has initiated discussions with the shipping industry and relevant stakeholders to explore potential solutions, such as dredging certain areas of the Canal to increase draft allowances. These efforts aim to ensure that the Canal remains a competitive route for LNG tankers and supports the growing global demand for cleaner energy sources.
Impact on Global Trade
The impact of challenges in the Panama Canal on global trade is significant and multifaceted. The Panama Canal plays a pivotal role in facilitating the movement of goods between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, and disruptions in its operations can have far-reaching consequences for international commerce. Here are some key ways in which the challenges in the Panama Canal impact global trade
- Delays and Disruptions: One of the most immediate and visible impacts of Canal challenges is delays in shipping schedules. Container ships, bulk carriers, and LNG tankers all experience longer waiting times, leading to delays in the delivery of goods to their destinations. This can disrupt supply chains, affecting businesses’ ability to meet customer demands promptly.
- Increased Costs: Longer transit times and delays result in increased shipping costs. Shipping companies often pass these added expenses onto consumers, leading to higher prices for imported goods. In some cases, businesses may absorb the additional costs, affecting their profit margins.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Many industries rely on just-in-time inventory systems to minimize storage costs and maximize efficiency. Delays in shipping can disrupt these systems, leading to shortages of critical components and impacting manufacturing and production processes worldwide. Industries like automotive and electronics, which require precise coordination of parts and components from various locations, are particularly vulnerable.
- Commodity Price Fluctuations: The challenges in the Panama Canal can affect the supply and demand dynamics of commodities. For example, disruptions in bulk carrier shipments can lead to fluctuations in the prices of grains, ore, and other bulk commodities. These price variations can impact industries that rely on stable commodity prices, such as agriculture and mining.
- Exploration of Alternative Routes: To mitigate the risks associated with Canal-related disruptions, some shipping companies and nations are exploring alternative trade routes. This includes using routes that bypass the Panama Canal entirely, such as the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa or the Northern Sea Route through the Arctic. These alternative routes can affect the profitability of the Canal and have geopolitical implications.
- Infrastructure Investments: Countries and companies affected by Canal challenges may invest in infrastructure projects to reduce their dependence on the Canal. For instance, countries like Brazil have been expanding their northern ports to accommodate larger bulk carriers and reduce reliance on the Canal for grain exports. These investments reshape global trade routes over the long term.
- Environmental Concerns: Longer shipping routes, such as circumnavigating South America, can result in increased fuel consumption and emissions. This is a significant concern as nations and industries are striving to reduce their carbon footprints. It highlights the environmental consequences of disruptions in Canal operations.
- Geopolitical Considerations: The Panama Canal’s importance extends beyond economics; it has geopolitical significance as well. Control over the Canal and its smooth operations can influence the strategic positioning of nations and alliances. Disruptions may lead to political tensions and diplomatic efforts to secure alternative routes.
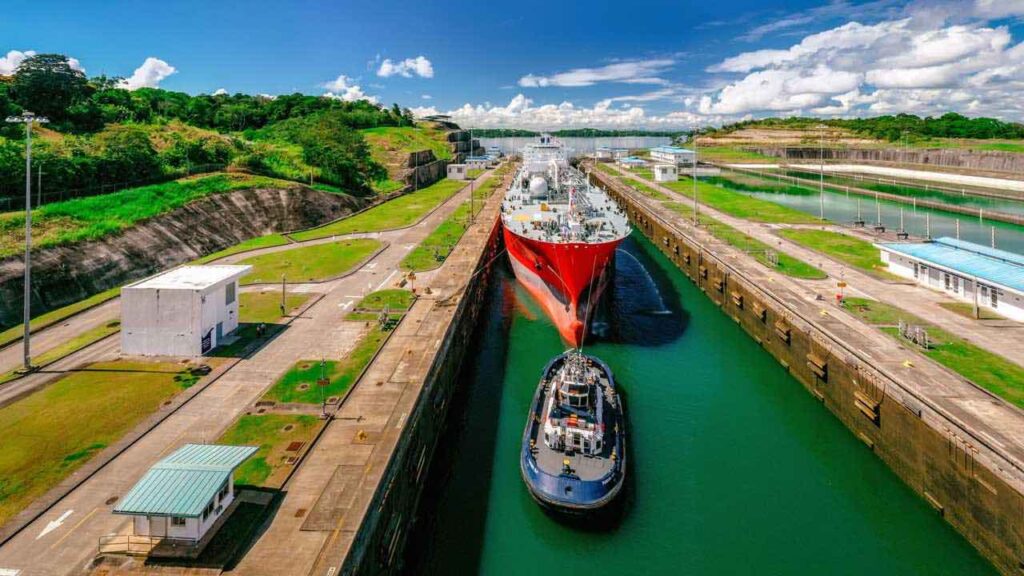

Conclusion
The Panama Canal, a linchpin of global maritime trade, is navigating significant challenges that are impacting shipping segments across the board. Container ships are grappling with congestion and rising costs, bulk carriers face draft restrictions, and LNG tankers contend with size limitations. These issues reverberate through the global supply chain, affecting businesses and consumers alike.
As the world continues to adapt to evolving trade dynamics, the future of the Panama Canal remains uncertain. However, it is clear that stakeholders from governments to shipping companies are actively engaged in finding solutions to ensure the Canal’s continued relevance in an ever-changing global economy. The outcomes of these efforts will shape the future of international trade for years to come.
Click here to join our Telegram chanel
You will get information, news, and support related to Merchant Navy.
