Navigating The Path To Net Zero: How The Global Shipping Industry Is Leading The Way

11 September 2023
Overview: Net Zero in Global Shipping
In the face of climate change, one industry stands as both a key contributor to the problem and a vital part of the solution: the global shipping industry. Responsible for transporting over 80% of the world’s goods, this industry is a cornerstone of our interconnected global economy. However, its environmental footprint is substantial, emitting a significant share of the world’s greenhouse gases. To combat climate change and work towards a net zero future, the global shipping industry is embarking on a transformative journey to reduce its carbon emissions and promote sustainability.
The Shipping Industry’s Environmental Challenge
The shipping industry’s contribution to climate change has long been a matter of concern. According to the International Maritime Organization (IMO), shipping accounts for nearly 3% of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. If left unchecked, these emissions are projected to increase substantially, potentially doubling or even tripling by 2050.
The industry faces unique challenges in reducing its environmental impact. Cargo ships are powered by large engines that predominantly rely on fossil fuels, primarily heavy fuel oil. Moreover, shipping routes traverse international waters, making it difficult to enforce stringent environmental regulations consistently. However, the urgency of the climate crisis has spurred global collaboration to address these challenges.
The Path to Net Zero Emissions
In recent years, the global shipping industry has made significant strides in its commitment to sustainability and reducing carbon emissions. Key strategies and initiatives include:
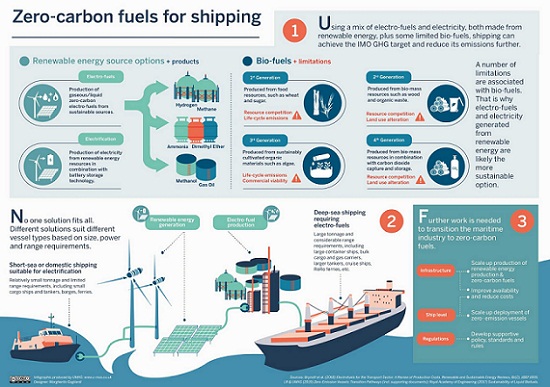
- Alternative Fuels: A transition towards cleaner fuels is underway. Many companies are exploring options like liquified natural gas (LNG), hydrogen, and ammonia as alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. Some have even experimented with wind-assisted propulsion systems to harness the power of nature.
- Energy Efficiency: Retrofitting existing vessels and designing new ships with energy-efficient technologies is crucial. Innovations like air lubrication systems and hull modifications are proven methods to reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Some shipping companies are investing in CCS technologies to capture and store CO2 emissions produced during the shipping process, effectively neutralizing their carbon footprint.
- Slow Steaming: Reducing ship speeds can significantly cut emissions. This practice, known as “slow steaming,” has become more prevalent, although it can impact supply chain schedules.
- Digitalization: Smart technologies and data analytics play a vital role in optimizing routes, weather forecasting, and fuel consumption, further reducing emissions.
- Emissions Reporting: The IMO’s mandatory data collection system requires ships of a certain size to report their fuel consumption and CO2 emissions, fostering transparency and accountability.
Regulation and International Cooperation
Addressing the shipping industry’s carbon footprint requires coordinated global efforts. The IMO’s Initial Strategy on Reducing GHG Emissions from Ships, adopted in 2018, outlines a clear trajectory towards reducing carbon emissions. This strategy aims to reduce the industry’s carbon intensity by at least 40% by 2030 and, ultimately, to achieve a 50% reduction in total annual GHG emissions by 2050 compared to 2008 levels.
International collaboration is essential in achieving these goals. The Poseidon Principles, a global framework for responsible ship finance, are gaining traction among financial institutions. These principles commit signatory banks to assessing and disclosing the climate alignment of their shipping portfolios.
Moreover, the transition towards greener shipping practices is being supported by various national governments and the European Union, which are implementing policies, incentives, and regulations to encourage sustainable shipping.
The Role of Innovation and Investment
Innovation and investment are key drivers of sustainability in the shipping industry. Governments, industry stakeholders, and investors are actively supporting research and development efforts focused on greener technologies. Initiatives such as the Green Shipping Program, which fosters public-private partnerships to develop and deploy green technologies, are becoming increasingly important.
Additionally, sustainable finance is playing a pivotal role. Investors are increasingly looking for opportunities that align with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. This trend is encouraging shipping companies to adopt cleaner practices and technologies, as they seek to attract responsible investment.
Challenges and Remaining Hurdles
While significant progress has been made, the global shipping industry faces several challenges on its path to net-zero emissions:
- High Costs: Transitioning to cleaner fuels and technologies can be expensive, and many shipping companies, especially smaller ones, may struggle to finance these changes.
- Infrastructure and Supply Chain: Building the infrastructure needed to support alternative fuels and technologies can be a logistical and financial challenge.
- Global Coordination: The industry’s international nature makes it challenging to implement consistent regulations and practices worldwide.
- Consumer Demand: Meeting consumer expectations for fast and reliable shipping while reducing emissions can be a delicate balancing act.
The Way Forward
The global shipping industry’s commitment to reducing its environmental impact is a positive step towards a sustainable future. With the support of governments, international organizations, and investors, it has the potential to become a leader in climate action.
To achieve the net-zero emissions target, the industry must continue to innovate, invest in sustainable practices, and collaborate on a global scale. The transition will undoubtedly require time and resources, but the cost of inaction is far greater.
In closing, the global shipping industry’s journey towards net-zero emissions is not just an environmental imperative; it is an economic and moral one. By embracing sustainability, the industry can contribute significantly to the global effort to combat climate change, ensuring that future generations inherit a healthier and more sustainable planet.
Click here to join our Telegram chanel
You will get information, news, and support related to Merchant Navy.
